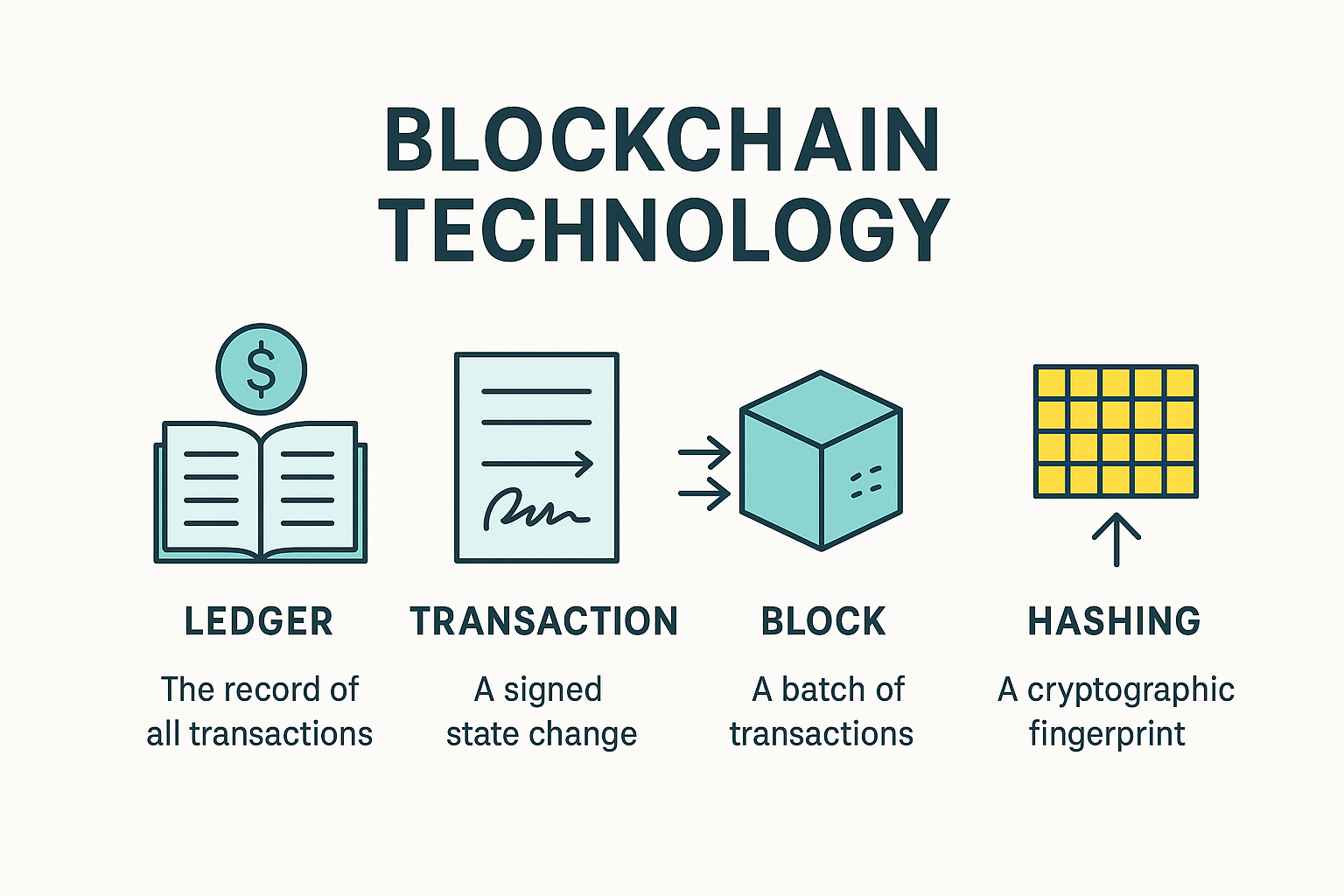
A blockchain is like a digital record book (ledger) that is stored on many computers instead of one.
- Every page in this book is called a block.
- These pages are linked together in order, making a chain of blocks (blockchain).
- Once written, you cannot erase or change past records.
Imagine a notebook that is photocopied and shared with thousands of people. If someone tries to cheat and change one page, it won’t match with everyone else’s copy, so the cheat fails.
How It Works in Crypto
Here’s the step-by-step process:
1. Transaction Starts
- Example: Ali wants to send 1 Bitcoin to Sara.
- Ali opens his crypto wallet (like a banking app), enters Sara’s address (her digital account number), and presses send.
- At this moment, Ali is saying to the network:
“I want to transfer 1 Bitcoin from me to Sara.”
2. Verification
- The network of computers (nodes) receives this request.
- These nodes check:
Does Ali actually have 1 Bitcoin in his wallet?
Has Ali already spent this Bitcoin before? (to avoid double spending) - If both answers are yes, the transaction is considered valid.
Think of it like a group of shopkeepers verifying if a customer’s cheque has money in the bank before accepting it.
3. Block Creation
- Valid transactions (Ali → Sara, John → Ayesha, etc.) are bundled together into a block.
- Each block is like a new page in the digital notebook.
- This page also contains:
- A timestamp (date & time)
- A reference (link) to the previous block
- A unique digital signature called a hash
It’s like stapling receipts together for the day and signing them to make sure no one can swap them later.
4. Consensus (Agreement by the Network)
- The network now needs to agree that this new block is correct.
- This is done through rules called consensus mechanisms:
- Proof of Work (Bitcoin): Computers solve tough puzzles. First one to solve gets rewarded.
- Proof of Stake (Ethereum 2.0, Cardano): People who hold coins lock them up to get a chance to validate and earn rewards.
5. Adding to Blockchain
- Once approved, the new block is permanently added to the chain.
- This creates a continuous history of all transactions, like a timeline that can’t be changed.
Think of signing a contract in front of witnesses. Once signed and filed, no one can secretly rewrite it.
6. Completion
- Now Sara officially receives the 1 Bitcoin.
- Both Ali and Sara can see the transaction on the blockchain (publicly visible, but identities remain hidden behind wallet addresses).
Blockchain in crypto is a shared, tamper-proof ledger that records transactions (like sending Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.) in a way that everyone can verify, but no one can secretly change.